Types of Low-Current Cables
Control Cables
With an operating voltage of 300/500 V and cross-sections ranging from 0.14 mm² to 2.50 mm², these cables use insulation materials such as PVC, HFFR, or PUR and are employed in industrial applications for signal transmission. In the communication sector, electronic circuits, measuring instruments, machine designs, office machines, computers, and audio systems, they can be easily applied in narrow spaces thanks to their flexible structure. Control cables are available in shielded or unshielded types and are used inside buildings.

Figure 1: Control cables are used as signal transmission cables in industrial applications.
Fire-Resistant Cables
With an operating voltage of 300/500 V, these cables are used in places with high human density or valuable assets such as smart or semi-smart buildings, hospitals, cinemas, theaters, schools, shopping centers, airports, factories, etc. They are employed in fire alarm systems, for the control/supply of devices that must operate during a fire, emergency lighting, operation of equipment required for monitoring and evacuation, and warning systems—systems that need to maintain their function for a certain period of time.

Figure 2: Fire-resistant cables are used in places with high human density to avoid harming human health during a fire and to ensure flawless transmission.
Coaxial Cables
With 50 Ohm and 75 Ohm impedance, these cables are used as distribution cables in indoor CATV, CCTV, cable TV, satellite, radio, and data communication systems where low attenuation is required. There are types produced for indoor use, outdoor overhead networks, underground installations, armored versions, and types manufactured according to military standards
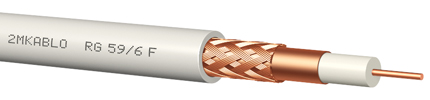
Figure 3: Coaxial cables are used in closed-circuit TV systems and in many studio applications for the transmission of video signals.
BUS Cables
PROFIBUS L2 cables are used for high-speed data transmission at rates such as 12 Mbit/s (Max. 100m). Since all machines are connected through a single BUS cable line, installation is easy and cost is low. They provide fast data exchange. These types of cables are designed for indoor and fixed applications.

Figure 5: BUS cables are used for communication between automation systems and for faster data transmission.
Internal Telephone and Fire Alarm Cables
They are manufactured in accordance with the TS 2814 standard and are used as central and subscriber distribution cables in fixed installations inside buildings. Types with PVC or HFFR outer sheaths, annealed tinned inner conductors, and shielded or unshielded versions are available.
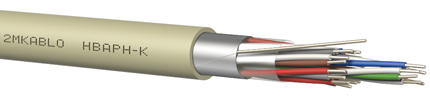
Figure 6: Telephone cables are used in fixed installations inside buildings.
Energy and Installation Cables
With an operating voltage ranging from 300 V to 1 kV, these cables can be single-core or multi-core. They are used in closed dry areas, distribution cabinets and panels, and fixed installations inside conduits, either under plaster or on the surface. Types are produced for use in places requiring higher operating temperatures (90°C), in indoor environments where mechanical stress is not excessive, as well as in outdoor applications underground and inside cable ducts. These types are resistant to sudden and short-term increases in operating temperature.
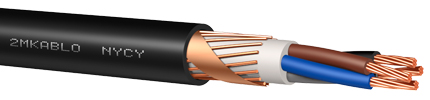
Figure 7: Energy cables are used in local cable networks and building electrical installations.
Instrumentation Cables
In process control and data processing, instrumentation cables are used for the transmission of analog and digital signals and have a wide range of applications. Factories, refineries, petrochemical plants, power stations, natural gas cycle/filling facilities, and industrial plants constitute the main application areas of these cables.

Figure 8: Instrumentation cables are used in measurement and control technology.
Marine and Yacht Cables
They are used in ship panels and electronic devices as fixed communication and instrumentation cables. Suitable for use in enclosed (protected) areas on all marine vessels.
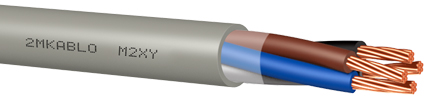
Figure 9: Marine yacht cables are used as fixed connection cables in ship panels and electronic devices.
Audio and Video Cables
These cables are used in audio and video systems such as professional studios, stage applications, broadcasting industry (TV and radio channels), conference halls, cultural centers, schools, cinemas, theaters, hotels, stadiums, audio equipment, and home audio/video applications. They are designed to provide high flexibility, low attenuation, and precise transmission of sound and image.

Figure 10: Audio and video cables are used not only in professional studios but also in places such as homes and schools for audio and video applications.
Unbalanced and Balanced Audio Cables
AES/EBU Cables
Analog and Digital Multicore Cables
Analog Video Cables
Digital Video and HD Cables Speaker Cables
HYBRID Cables
LMP Cables
Multi Video and RGB Cables
Star-quad Cables
TRIAX and TRIFLEX Cables
TWIN and Walkman Cables
VCC / Combined Cables
Apart from these, there are also types such as Railway Cables, Silicone Cables, and Welding Cables. The variety of low-current cables is increasing day by day due to reasons such as the transformation of buildings into new smart systems, developments in energy production facilities using solar, wind, and nuclear power, the rise of automation in industrial enterprises, the spread of information systems and new technologies, and globalization.
Electrical Tests
Considering the areas of cable usage, the durability they provide against possible risks is highly important. For this reason, tests conducted on cables give the most accurate durability results. Since cables are used in buildings, hospitals, cinemas, theaters, schools, shopping centers, airports, factories, tunnels, etc.—places that are central to life—they must have properties such as non-flame propagation, non-spreading, low smoke density, and absence of toxic and corrosive gases. Only through tests performed on them can these durability features be confirmed.
In this content, we will look at the electrical tests carried out in 2M Cable laboratories:
- High Voltage – EN 50395, IEC 60502-1
- Transfer Impedance and Screening Attenuation – IEC 62153-4-3, IEC 62153-4-4
- Conductor Resistance Measurement – IEC 60228
- Coaxial Cable – EN 50117-2-4
High Voltage – EN 50395, IEC 60502-1
The insulation strength of cables under high voltage is tested. The test duration is 5 minutes. Each conductor of the cable is expected to withstand high voltage of 3,500 Volts at 50 Hz. It is determined whether there is a short circuit in the conductors under high voltage.
Transfer Impedance and Screening Attenuation – IEC 62153-4-3, IEC 62153-4-4
This test measures the shielding quality of the cable. A 1-meter sample is used for transfer impedance. A 3-meter sample is used for screening attenuation measurement. Transfer impedance and screening attenuation are measured at different frequency ranges. In both measurements, the screening attenuation graph is interpreted.
Conductor Resistance Measurement – IEC 60228
In this test, the resistance of the copper used as the conductor in cables is measured. The conductor is placed in the test setup and its resistance is measured with the help of a milliohmmeter.
Coaxial Cable – EN 50117-2-4
Measurements are made using a Network Analyzer test device. The reduction of the produced signal at different frequencies is measured in decibels (dB). The return loss caused by irregularities and imbalances in the cable is measured.